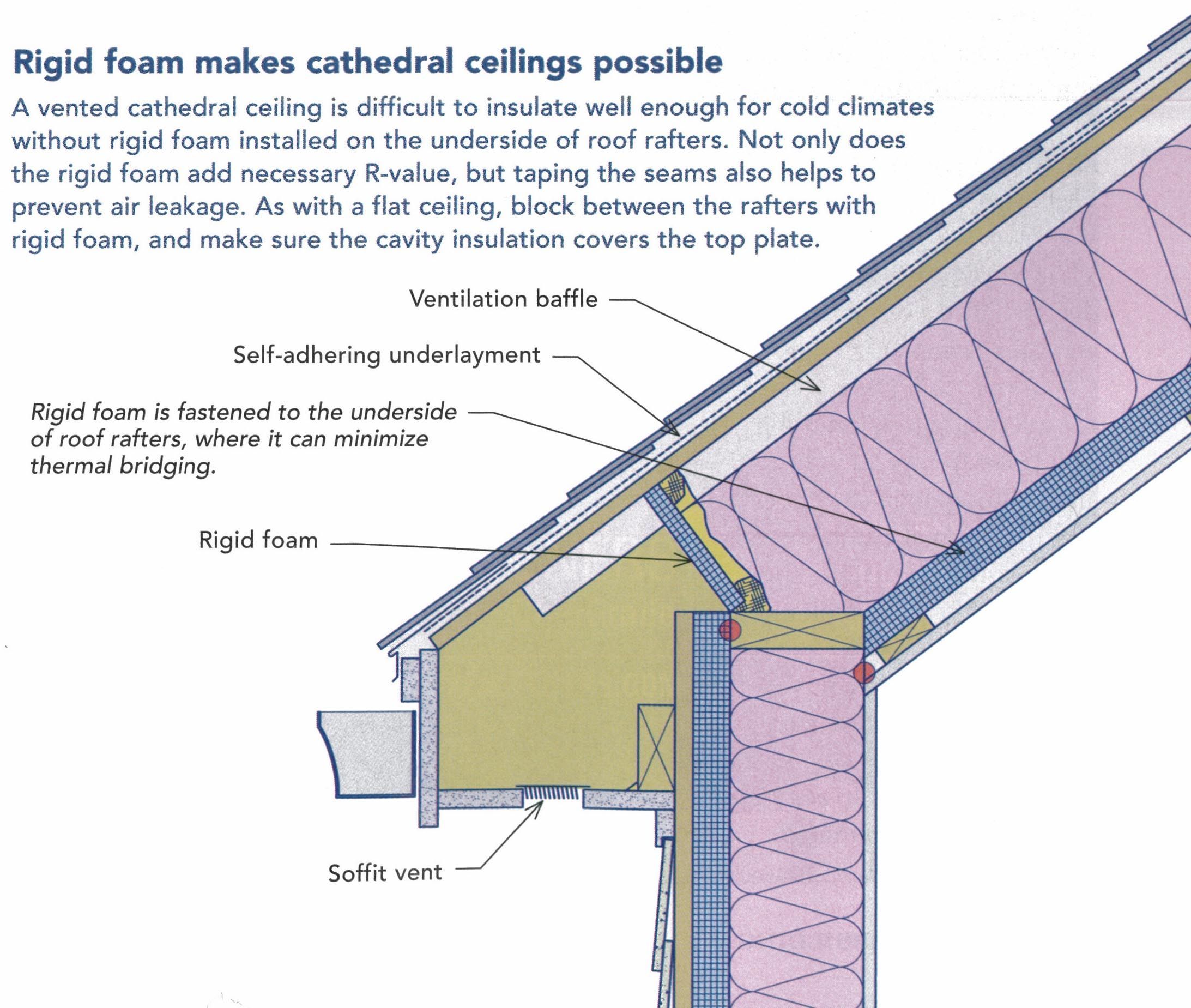
Cold Flat Roof Ventilation Detail

The minimum requirements for cold roof ventilation are set out in bs 5250 control of condensation in buildings which takes into consideration span pitch and roof area.
Cold flat roof ventilation detail. There are two types of flat roof systems warm and cold roofs which affect the positioning of the ventilation. Cold roofs have the waterproof layer placed directly onto the roof deck and the insulation inside the roof just above the ceiling. Why don t cold roofs need to be ventilated. That means the rest of the roof is protected from heat.
2011 code of practice for control of condensation in buildings stipulates that there should be a ventilation gap between the insulation and the bottom of the flat roof deck of at least 50mm. The wider the span the more free airflow is required in the roof space. This video shows the key features of a flat roof cold deck construction and how to draw the details to a scale of 1 10. Flat roof ventilation allows for the circulation of air in the property particularly for warmer rooms in residential buildings.
A warm deck roof is where the insulation is placed on top of the rafters joists and the roof covering is then placed over the insulation. No ventilation is required for these types of roofs. In this case ventilation is required and the roof can still become wet with condensation which may cause materials to decay. When thermal insulation is placed below the deck the ventilation must also be on the underside.
There are two types of flat roof. A cold roof is the most common type of roof construction often taking the form of an uninhabited storage space. A cold roof system sees the insulation placed immediately above the ceiling between the joists with ventilation space above the insulation. Their layer of insulation is beneath the roof decking and the roofing membranes.
Cold roofs and warm roofs. A cold roof really is colder than the rest of your home in the winter which means condensation is much less likely to develop. Ventilation for cold roofs.